DNS is used to translate between a human-readable name like poftut.com and IP address like 45.79.1333.118. DNS can use both UDP and TCP protocols but generally, UDP protocol is preferred. In this tutorial, we will learn how to flush, clear the DNS cache with ipconfig /flushdns command. This tutorial can be applied to the All Windows Operating system versions like Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019 without a problem. This will not require special privileges like Administrator.
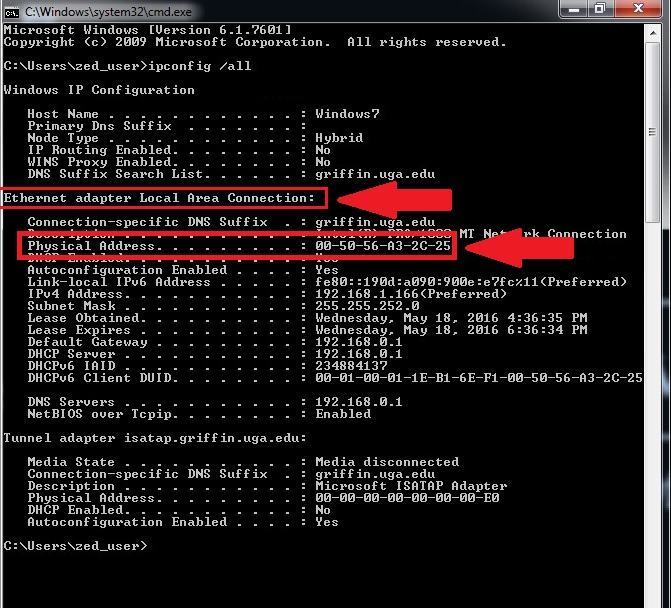
- The ipconfig command: The default information that this tool will show you will be the following: The IP address, The subnet mask; The default gateway. The information will be shown for each adapter that is bound to TCP/IP. This is an example of ipconfig default output.
- Displays the network configuration, refresh DHCP and DNS settings. Used without parameters, ipconfig will display the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Ipconfig - IP configuration command - Windows CMD - SS64.com SS64.

What Is DNS Cache?
For every domain name, DNS will query the DNS Server normally. But this may create a bottleneck in busy times. In order to prevent this bottleneck, DNS services use a cache mechanism. Learned DNS records are stored in a cache for some time. If during this period a DNS is queried cache returns if exists.
Print and List Current DNS Cache Entries
At the command prompt, run the following commands in the listed order, and then check to see if that fixes your connection problem: Type netsh winsock reset and press Enter. Type netsh int ip reset and press Enter. Type ipconfig /release and press Enter. Type ipconfig /renew and press Enter. Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter. Ipconfig is a TCP/IP utility that displays the current TCP/IP configuration settings for each network interface card (NIC). The ipconfig command is often one of the first commands to use when to check the status of the connection when you experience communication problems on a TCP/IP network.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2019-03-19_16h09_50-5c914cb946e0fb0001770166.png)
Ipconfig Is Not A Recognized Command
We can print or list currently cached DNS entries with the /displaydns option of ipconfig command.
As we can see from screenshot domain names are stored in DNS cache with related information. There is the following information
- Record Name specifies the name of the DNS record
- Record Type specifies the type of DNS entry
- Time To Live provides the validity time of the DNS entry
- Data Length
- Section
Flush DNS Entries with ipconfig /flushdns Command
In order to clear this DNS cache, we will use ipconfig command with /flushdns parameter. This will remove all DNS entries except localhost because it is a local system DNS record.
We can see that flush is completed successfully from the screenshot.
Flush DNS Cache From Run Box
In the previous example, we have used a command line which is named cmd.exe. We can also run ipconfig /flushdns command from Run like below. This will open a command line and run the command to clear and delete all DNS cache entries. Then the command line will be closed automatically.
Check DNS Cache Entries Whether Flushed
We can check whether flush is effective with the ipconfig /displaydns command again like below.
As we can see other DNS entries are deleted successfully. There are only localhost and arpa DNS entries which are static.

Flush DNS Cache with Clear-DnsClientCache PowerShell Command
PowerShell provides very same of the traditional MS-DOS commands. We can use all of the MS-DOS commands in PowerShell too. We can flush the DNS cache records with the ipconfig /flushdns command like below. First, we will open PowerShell from the start menu by writing powershell like below.
Ipconfig Vs Ipconfig All
Then we will type the command like below.
Flush DNS with PowerShell Clear-DnsClientCache Cmdlet
Ipconfig Renew
Powershell provides a new way to clear DNS client cache or flush DNS with the Clear-DnsClientCache cmdlet. We will just execute the command below.